Shoulder Pain: Unraveling the Knots of Discomfort and Exploring Effective Relief Strategies.
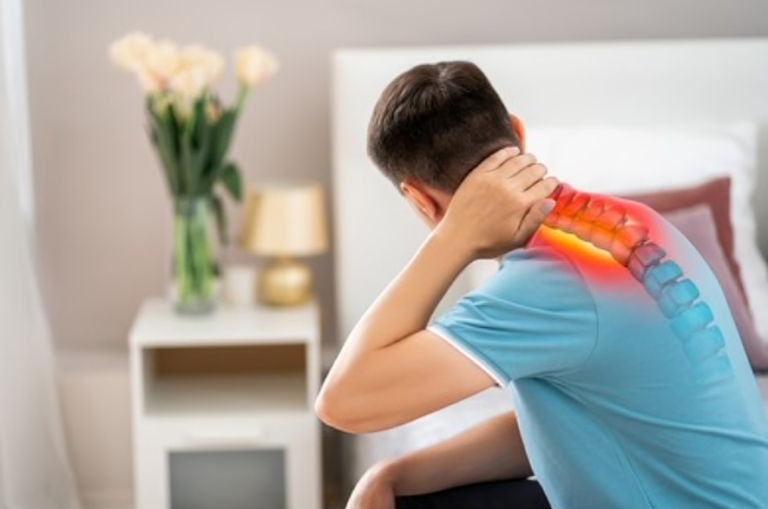
Shoulder pain, a pervasive and often debilitating ailment, can disrupt daily activities and diminish overall quality of life. Whether stemming from overuse, injuries, or underlying medical conditions, understanding the intricacies of shoulder pain is crucial for finding effective relief. In this article, we will delve into the causes, and explore a range of strategies to alleviate shoulder discomfort and restore mobility.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Causes of Shoulder Pain
- Muscle Strain and Overuse:
- Prolonged or repetitive activities, such as heavy lifting or certain sports, can strain the shoulder muscles, leading to pain and discomfort.
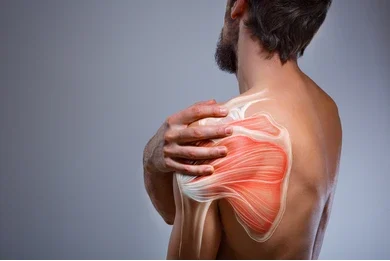
- Rotator Cuff Injuries:
- Injuries to the rotator cuff, a vital group of muscles and tendons supporting the shoulder joint, can result in pain and restricted movement.
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis):
- A condition marked by the tightening of the shoulder joint capsule, often caused by prolonged immobility or underlying medical issues.
- Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the shoulder joint, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
- Tendinitis:
- Inflammation of the tendons, commonly caused by overuse or aging, can lead to tendinitis and shoulder pain.
Symptoms of Shoulder Pain
- Pain and Discomfort:
- The primary and often most noticeable symptom ranges from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing pain.
- Limited Range of Motion:
- Difficulty in performing daily activities or raising the arm due to pain and stiffness.
- Swelling and Redness:
- Inflammation in the shoulder joint may result in visible swelling and redness.
- Weakness:
- Muscle weakness in the shoulder area, affecting everyday tasks.
Effective Relief Strategies
- Rest and Ice:
- Allow the shoulder to rest and apply ice to reduce inflammation and soothe pain.
- Physical Therapy:
- Targeted exercises to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility are particularly beneficial for rotator cuff injuries and frozen shoulders.
- Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or pain relievers to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections:
- In severe cases, injections may be recommended to alleviate inflammation directly.
- Surgery:
- Surgical intervention for conditions like rotator cuff tears or advanced arthritis that do not respond to conservative treatments.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion
Understanding the root causes and symptoms of shoulder pain is crucial for effective management. By adopting a personalized approach that may include rest, therapy, medications, or surgery, individuals can navigate the journey to relief and restore shoulder function. If shoulder pain persists or worsens, seeking professional medical advice ensures a comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plan, ultimately unraveling the knots of discomfort and fostering a path toward improved shoulder health.