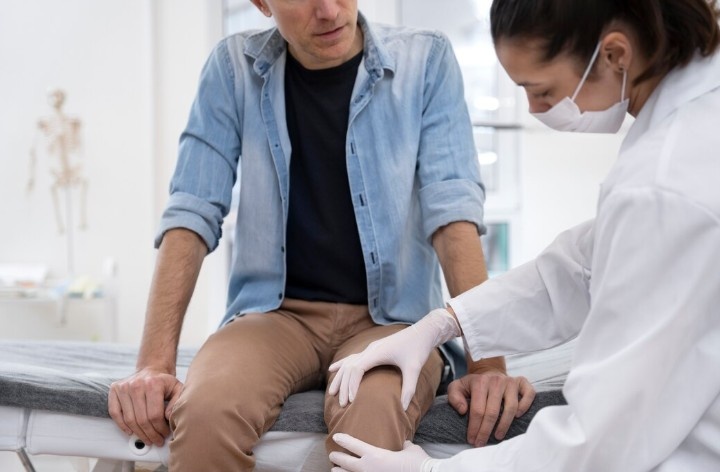
Managing Knee Pain In Athletes And Active Individuals
Knee pain is a common concern among athletes and active individuals, impacting performance and quality of life. Whether you’re a professional athlete or a recreational runner, knee pain can hinder your ability to participate in sports and activities you love. However, with the right approach to management and treatment, it’s possible to alleviate discomfort and prevent further injury. In this article, we’ll explore effective strategies for managing knee pain in athletes and active individuals, enabling them to continue pursuing their passions with confidence.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Understanding the Causes
Before diving into management strategies, it’s crucial to understand the potential causes of knee pain in athletes and active individuals. Common culprits include overuse injuries, such as runner’s knee (patellofemoral pain syndrome) and iliotibial (IT) band syndrome, as well as acute injuries like ligament sprains and meniscus tears. Additionally, factors such as improper biomechanics, muscle imbalances, and inadequate warm-up or cool-down routines can contribute to knee discomfort during physical activity.
Seeking Professional Evaluation
When experiencing persistent or severe knee pain, athletes and active individuals should seek professional evaluation from a healthcare provider specializing in sports medicine or orthopedics. A thorough examination, including a review of medical history and diagnostic tests such as X-rays or MRI scans, can help identify the underlying cause of knee pain. This allows for personalized treatment planning tailored to the individual’s needs and goals.
Rest and Recovery
One of the initial steps in managing knee pain is to allow the affected joint to rest and recover. This may involve temporarily modifying or reducing the intensity and duration of athletic training or activities that exacerbate symptoms. Incorporating low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling can help maintain cardiovascular fitness while minimizing stress on the knees. Adequate rest allows the body’s natural healing processes to take place and prevents further aggravation of the injury.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the rehabilitation of knee injuries and the prevention of future occurrences. A skilled physical therapist can design a customized exercise program focused on strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee, improving flexibility, and correcting biomechanical issues. Modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and manual therapy techniques may also be utilized to alleviate pain and promote tissue healing. Consistent adherence to a structured rehabilitation plan is essential for optimal outcomes.
Bracing and Supportive Devices
In some cases, wearing a knee brace or supportive device during athletic activities can provide stability and reduce stress on the injured joint. Bracing options range from simple sleeve-style braces for mild support to more rigid braces designed for ligament injuries or post-operative rehabilitation. Proper fitting and selection of the appropriate brace should be guided by a healthcare professional to ensure effectiveness and comfort.
Addressing Biomechanical Factors
Addressing underlying biomechanical factors is crucial for the long-term management of knee pain in athletes and active individuals. This may involve gait analysis to identify abnormalities in walking or running mechanics, followed by corrective measures such as orthotic inserts or footwear modifications. Strengthening exercises targeting specific muscle groups, particularly the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, can help improve biomechanical alignment and reduce stress on the knees during physical activity.
Nutrition and Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for reducing the load placed on the knees and preventing excessive wear and tear. Athletes and active individuals should focus on a balanced diet rich in nutrient-dense foods to support overall health and recovery from injury. Adequate hydration is also important for joint lubrication and optimal athletic performance. Additionally, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish, leafy greens, and berries may help alleviate knee pain associated with inflammation.
Incorporating Cross-Training and Variety
To prevent overuse injuries and promote overall fitness, athletes and active individuals should incorporate cross-training and variety into their exercise routines. This may involve alternating between different types of activities, such as swimming, cycling, and strength training, to reduce repetitive stress on the knees and promote muscular balance. Cross-training not only allows for active recovery but also helps maintain motivation and enjoyment in physical activity.
Conclusion
Managing knee pain in athletes and active individuals requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying causes while promoting healing and prevention. By seeking professional evaluation, implementing rest and recovery strategies, engaging in physical therapy, addressing biomechanical factors, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and incorporating cross-training, individuals can effectively manage knee pain and continue pursuing their athletic endeavors with confidence and resilience. Remember, listening to your body and prioritizing self-care are key components of long-term knee health and optimal performance.
Also, Follow us on Instagram