Shoulder Pain In Athletes: Causes, Treatment, And Prevention
Shoulder pain is a common complaint among athletes, ranging from recreational enthusiasts to elite professionals. The shoulder is a complex joint, highly mobile yet inherently unstable, making it susceptible to various injuries and conditions. Athletes engage in repetitive motions and high-intensity activities that put significant strain on the shoulder, increasing the risk of pain and injury. Understanding the causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies for shoulder pain in athletes is crucial for optimizing performance and preventing long-term damage.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Causes of Shoulder Pain in Athletes
Overuse Injuries: Athletes involved in sports such as swimming, tennis, baseball, and volleyball often experience shoulder pain due to overuse. Repetitive overhead motions can lead to inflammation, tendonitis, and muscle strains in the shoulder.
Traumatic Injuries: Contact sports like football, rugby, and martial arts carry a risk of traumatic shoulder injuries, including dislocations, fractures, and ligament tears. These injuries often result from collisions, falls, or sudden impacts.
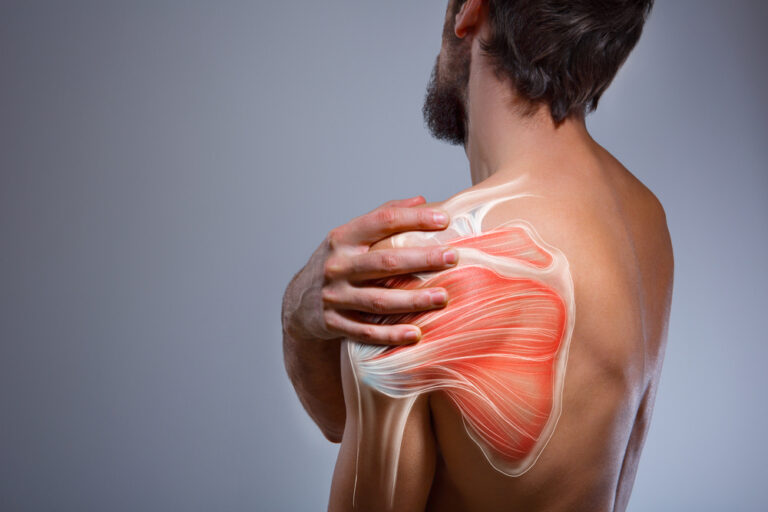
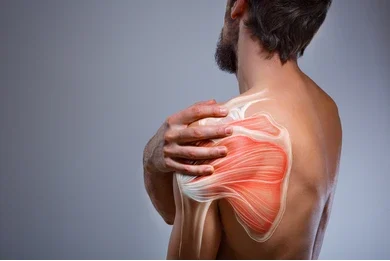
Rotator Cuff Tears: The rotator cuff comprises a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. Athletes may develop rotator cuff tears from repetitive stress, aging, or acute trauma, leading to pain, weakness, and limited range of motion.
Labral Tears: The labrum is a ring of cartilage that lines the rim of the shoulder socket, providing stability to the joint. Athletes involved in throwing sports or those who perform repetitive overhead activities are prone to labral tears, which can cause pain, clicking sensations, and instability.
Poor Biomechanics: Incorrect technique or faulty biomechanics during sports activities can place excessive stress on the shoulder joint, predisposing athletes to injury. Factors such as muscle imbalances, poor posture, and inadequate warm-up may contribute to shoulder pain.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Pain
Rest and Activity Modification: Temporary cessation of activities that aggravate shoulder pain is essential to allow healing and prevent further damage. Athletes may need to modify their training routines or switch to low-impact exercises during the recovery period.
Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises aimed at improving strength, flexibility, and shoulder stability are vital for athletes with shoulder pain. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to address specific weaknesses and imbalances.
Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen may be prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation associated with shoulder injuries. However, long-term use should be closely monitored due to potential negative effects.
Injection Therapy: Corticosteroid injections may be recommended for athletes with severe pain and inflammation who do not respond to conservative treatments. These injections can provide immediate relief but are not a permanent cure.
Surgery: In cases of severe or persistent shoulder pain, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged tissues or stabilize the joint. Arthroscopic procedures, such as rotator cuff repair or labral reconstruction, are minimally invasive techniques that offer faster recovery times for athletes.
Prevention Strategies for Shoulder Pain
Proper Technique: Athletes should receive proper instruction on technique and biomechanics specific to their sport. Correct body mechanics can reduce the risk of shoulder injuries and enhance performance.
Gradual Progression: Gradually increasing the intensity, duration, and frequency of workouts can assist athletes avoid overuse problems. Avoid sudden spikes in workload that can overload the shoulder joint and lead to injury.
Strength and Conditioning: Incorporating shoulder-specific strength training exercises into the workout regimen can improve muscle balance and stability, reducing the risk of injury. Focus on exercises targeting the rotator cuff, deltoids, and scapular stabilizers.
Warm-Up and Stretching: A thorough warm-up routine before engaging in sports activities prepares the muscles and joints for movement and reduces the risk of injury. Dynamic stretches targeting the shoulders, neck, and upper back can enhance flexibility and mobility.
Proper Equipment: Using appropriate sports equipment, such as protective padding, braces, or supportive gear, can help prevent traumatic injuries to the shoulder joint. Ensure that equipment fits properly and is in good condition.
In conclusion
shoulder pain is a common issue affecting athletes across various sports disciplines. Understanding the underlying causes, implementing effective treatment strategies, and adopting preventive measures are essential for managing shoulder pain, optimizing athletic performance, and ensuring long-term shoulder health. By prioritizing proper technique, conditioning, and injury prevention strategies, athletes can reduce the risk of shoulder injuries and enjoy their sport safely and effectively.
Also, Follow us on Instagram