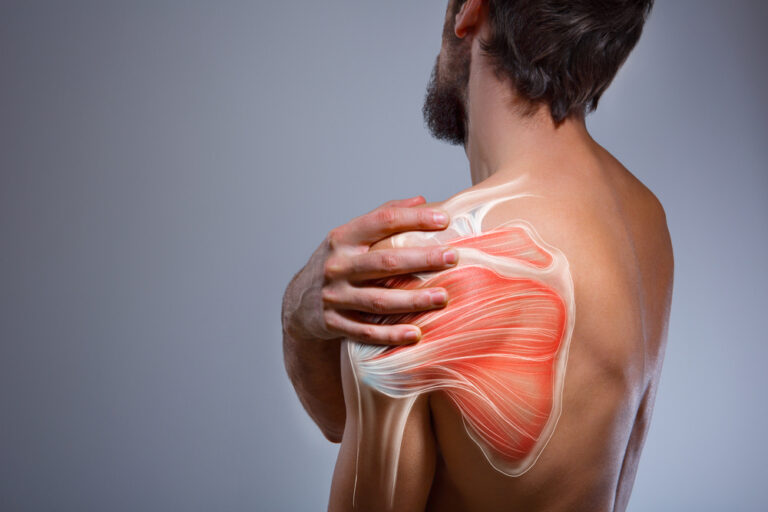
The Complex Web of Nerve Pain: Understanding, Coping, and Seeking Relief.
Nerve pain, medically known as neuropathic pain, is a complex and often debilitating condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Unlike typical pain, which stems from injuries or inflammation in tissues, nerve pain arises from dysfunction or damage to the nervous system. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of nerve pain, its causes, symptoms, and various approaches to managing and seeking relief from this challenging condition.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Understanding Nerve Pain
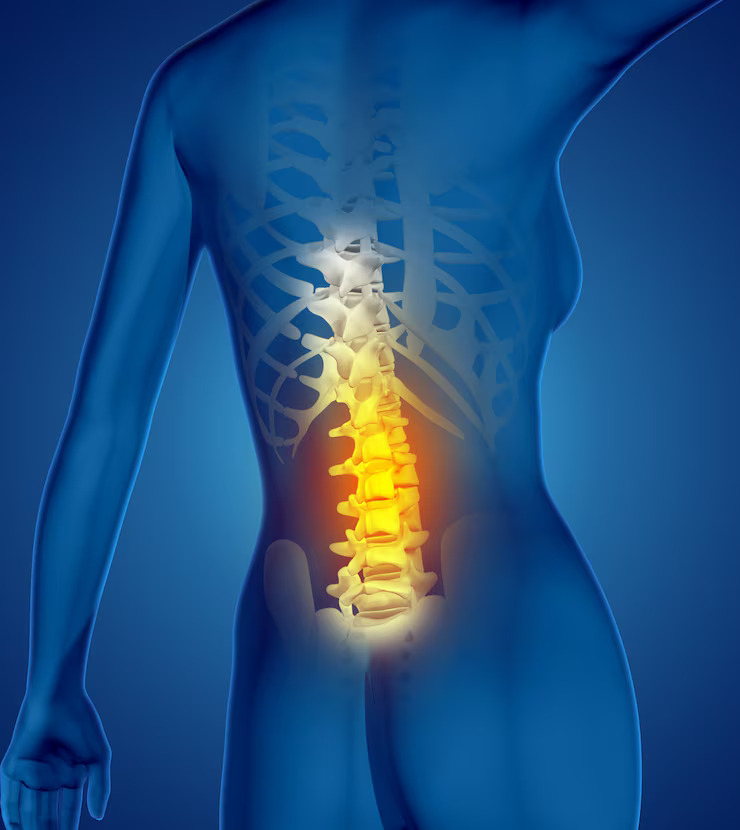
Nerve pain is characterized by a sharp, stabbing, burning, or shooting sensation that can be chronic or intermittent. Unlike nociceptive pain, which is a response to injury or inflammation, neuropathic pain originates from malfunctions in the nervous system. The nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (network of nerves throughout the body).
Common Causes of Nerve Pain
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Peripheral neuropathy is a prevalent cause of nerve pain, often associated with conditions like diabetes, chemotherapy, or certain infections. It involves damage to the peripheral nerves, leading to sensations of tingling, numbness, or pain in the extremities.
- Nerve Compression: Conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome or sciatica can cause nerve compression, leading to pain and discomfort along the affected nerve pathways.
- Injuries: Traumatic injuries, especially those affecting nerves directly, can result in persistent nerve pain. Surgical procedures and accidents are common triggers for post-injury neuropathic pain.
- Shingles (Herpes Zoster): The varicella-zoster virus, responsible for chickenpox, can cause shingles later in life. Shingles can lead to a painful condition known as postherpetic neuralgia, where nerve pain persists even after the rash has healed.
Symptoms of Nerve Pain
- Burning Sensation: A common hallmark of nerve pain is a persistent burning sensation that can be localized or radiate along the affected nerve pathways.
- Tingling and Numbness: Many individuals with nerve pain experience tingling or numbness, often described as a “pins and needles” sensation.
- Electric Shock-like Sensations: Some people may describe nerve pain as sudden, sharp electric shock-like sensations that can be triggered by movement or touch.
- Increased Sensitivity: Hyperalgesia, or heightened sensitivity to pain, is another common symptom of nerve pain. Everyday stimuli that are typically not painful can become intensely uncomfortable.
Coping Strategies and Management
- Medications: Antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and certain pain medications may be prescribed to manage nerve pain. These medications work by modulating the way nerves transmit signals.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve mobility, address muscle imbalances, and reduce the impact of nerve pain on daily activities.
- Topical Treatments: Creams or patches containing analgesic medications, such as lidocaine or capsaicin, can provide localized relief for nerve pain.
- Nerve Blocks: In some cases, nerve blocks involving the injection of anesthetic agents can temporarily alleviate nerve pain by disrupting the pain signals.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing stress, can contribute to overall well-being and may help alleviate nerve pain symptoms.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion
Nerve pain poses a multifaceted challenge, impacting individuals on physical, emotional, and psychological levels. While there may not be a one-size-fits-all solution, a combination of medical interventions, therapeutic approaches, and lifestyle modifications can offer relief and improve the quality of life for those grappling with nerve pain. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, including pain specialists and neurologists, is crucial in developing a personalized and effective management plan tailored to the specific causes and manifestations of nerve pain.