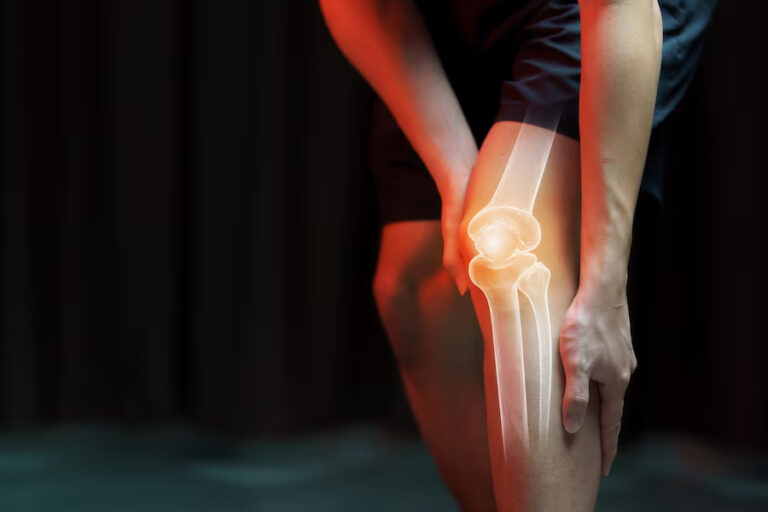
Understanding and Managing Knee Pain Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options.
Knee pain is a prevalent and often debilitating condition that can affect individuals of all ages and lifestyles. Whether caused by injury, overuse, or underlying medical conditions, knee pain can significantly impact one’s quality of life. This article aims to explore the common causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available to alleviate knee pain and improve overall knee health.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
- Injuries:
- Sprains and Strains: Overstretching or tearing of ligaments and muscles around the knee can lead to pain and reduced mobility.
- Torn Meniscus: The meniscus, a rubbery cartilage in the knee, can tear due to sudden twisting motions or degeneration over time.
- Medical Conditions:
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease that occurs when the protective cartilage in the knee wears down, causing pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder that affects the joints, leading to inflammation and pain in the knees.
- Gout: The accumulation of uric acid crystals in the knee joint can cause sudden and intense pain.
- Overuse and Wear-and-Tear:
- Patellar Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone, often seen in athletes involved in jumping sports.
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS): Overuse of the iliotibial band, a thick band of tissue running from the hip to the outer knee, can result in pain on the outer side of the knee.
Symptoms of Knee Pain
- Pain: Ranging from mild discomfort to severe, sharp pain.
- Swelling: Inflammation and fluid buildup in and around the knee joint.
- Stiffness: Difficulty in bending or straightening the knee.
- Redness and Warmth: Signs of inflammation, particularly in cases of arthritis or infection.
- Popping or Clicking Sounds: May indicate structural issues or cartilage damage.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
- Rest and Ice:
- RICE Method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation): Initial treatment for acute injuries to reduce swelling and pain.
- Medications:
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter or prescription medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: For more severe inflammation, injections may be recommended to reduce pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy:
- Customized exercise programs to strengthen muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and enhance overall joint function.
- Bracing and Support:
- Knee Braces: Provide stability and support for individuals with certain conditions or after injuries.
- Invasive Procedures:
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to diagnose and treat various knee conditions.
- Joint Replacement: In cases of severe arthritis, joint replacement surgery may be considered for long-term relief.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight Management: Excess weight can exacerbate knee pain, so maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate stress on the joints.
- Low-Impact Exercise: Activities like swimming or cycling can help maintain joint mobility without causing excessive strain.
Conclusion
Effective management of knee pain requires a thorough understanding of its underlying causes and appropriate intervention strategies. Seeking prompt medical attention, adopting a holistic approach to treatment, and making lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve the overall health and function of the knees. It’s essential for individuals experiencing knee pain to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.