Exercise And Physical Therapy For Joint Pain Management
Joint pain can significantly impact daily life, causing discomfort, limited mobility, and decreased quality of life. While medication can provide relief, exercise and physical therapy offer long-term solutions by strengthening muscles, improving flexibility, and promoting overall joint health. In this article, we explore the role of exercise and physical therapy in managing joint pain effectively.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Understanding Joint Pain
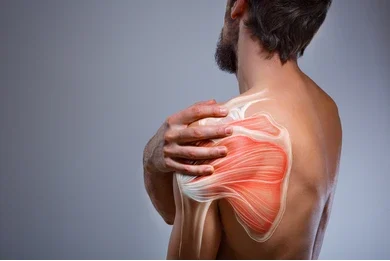
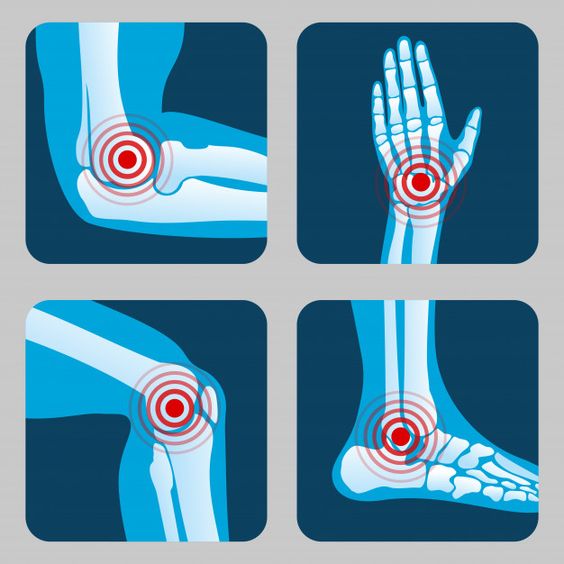
Joint pain can arise from various factors, including arthritis, injury, overuse, or age-related degeneration. Commonly affected joints include the knees, hips, shoulders, and spine. Regardless of the cause, joint pain often leads to stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion, hindering normal activities.
The Role of Exercise
Contrary to common belief, engaging in appropriate exercises can alleviate joint pain and enhance joint function. Exercise helps maintain joint flexibility, strengthens supporting muscles, and improves overall joint stability. Additionally, regular physical activity can aid in weight management, reducing the burden on weight-bearing joints.
Types of Exercises for Joint Pain Management
- Low-Impact Aerobic Exercises: Activities like swimming, cycling, and brisk walking provide cardiovascular benefits without placing excessive stress on the joints. These exercises improve circulation, promote joint lubrication, and enhance overall fitness levels.
- Strength Training: Targeting specific muscle groups around the affected joints through resistance exercises can alleviate pain and enhance joint stability. Incorporating exercises with resistance bands, free weights, or weight machines helps build strength and protect joints.
- Flexibility and Range-of-Motion Exercises: Stretching exercises improve joint flexibility, reduce stiffness, and enhance mobility. Gentle stretching routines, yoga, and tai chi can alleviate tension in the muscles and promote relaxation, easing joint discomfort.
- Balance and Stability Training: Balance exercises, such as standing on one leg or using balance boards, help improve proprioception and prevent falls, especially crucial for individuals with joint pain, as falls can exacerbate existing issues.
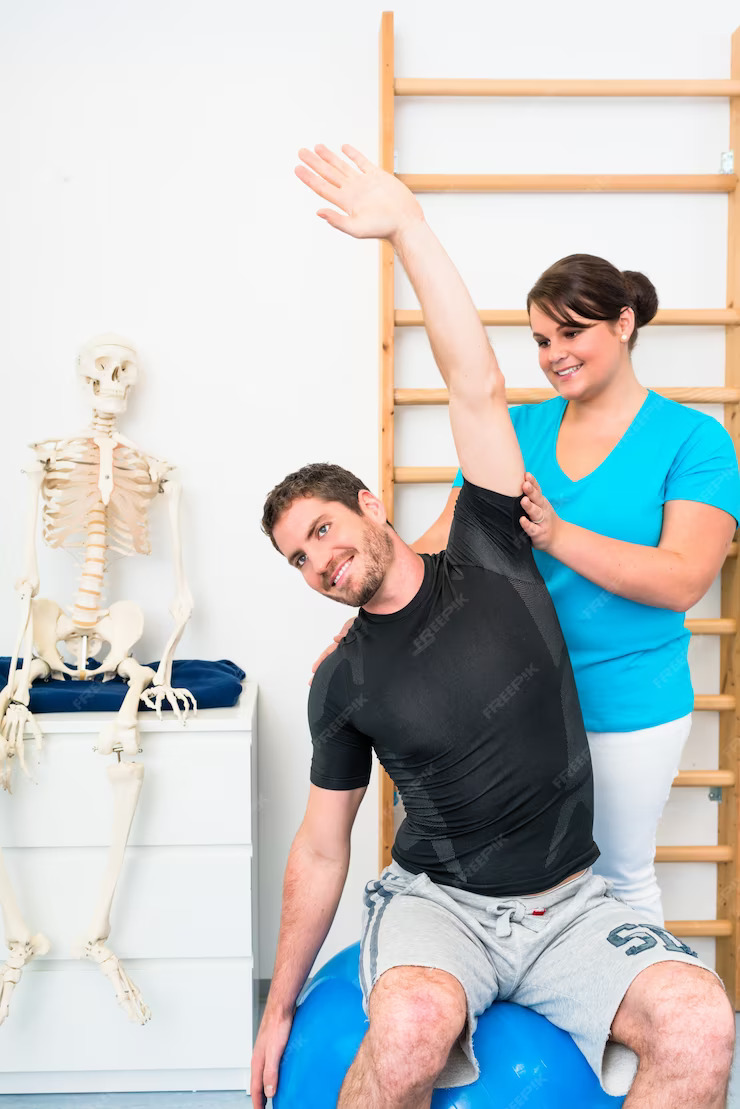
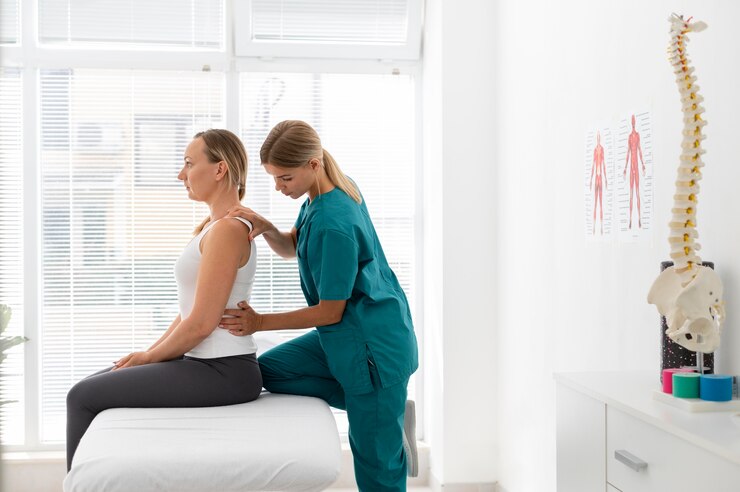
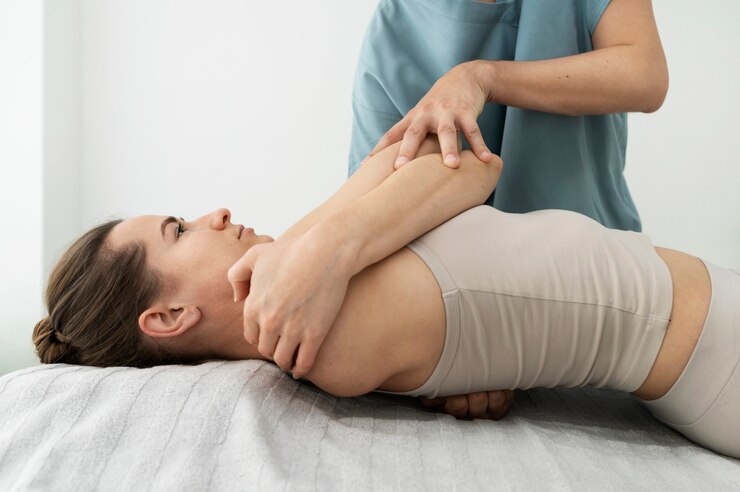
The Role of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in joint pain management by tailoring exercises and interventions to individual needs. A skilled physical therapist assesses joint function, identifies areas of weakness or imbalance, and develops personalized treatment plans to address specific concerns. Physical therapy sessions may include manual therapy techniques, modalities like heat or cold therapy, and guidance on proper body mechanics and posture.
Benefits of Exercise and Physical Therapy:
- Pain Reduction: Regular exercise and physical therapy can reduce joint pain by strengthening supporting muscles, improving joint stability, and promoting proper alignment.
- Improved Functionality: Enhanced joint mobility and muscle strength translate to improved functionality in daily activities, allowing individuals to perform tasks with greater ease and confidence.
- Prevention of Further Damage: By addressing underlying weaknesses and imbalances, exercise and physical therapy help prevent further joint degeneration and reduce the risk of future injuries.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: As joint pain diminishes and functionality improves, individuals experience an overall enhancement in their quality of life, enjoying greater independence and participation in activities they love.
In conclusion
exercise and physical therapy are invaluable tools in the management of joint pain. By incorporating appropriate exercises and seeking guidance from a qualified physical therapist, individuals can alleviate pain, improve joint function, and regain control over their lives. Remember, consistency and patience are key, and always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have existing health conditions or concerns related to joint pain.
Also, Follow us on Instagram