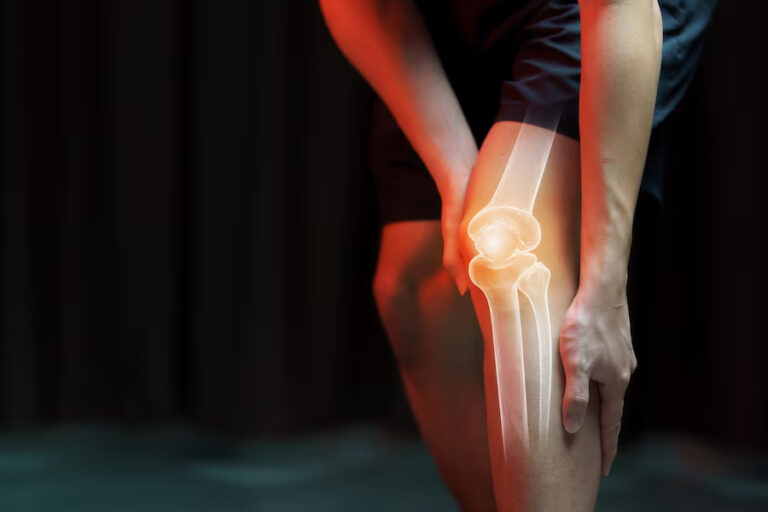
Understanding and Managing Knee Pain: A Comprehensive Guide.
Knee pain is a common ailment that affects people of all ages, impacting mobility and overall quality of life. Whether caused by injury, overuse, or underlying medical conditions, knee pain can be a challenging and persistent issue. In this article, we explore the various causes of knee pain, potential risk factors, and effective strategies for managing and alleviating discomfort.
Common Causes of Knee Pain:
- Osteoarthritis: One of the most prevalent causes of knee pain, osteoarthritis occurs when the protective cartilage in the knee joint wears down over time. This can result in pain, swelling, and stiffness, particularly during movement.
- Injuries: Traumatic injuries, such as ligament tears (e.g., anterior cruciate ligament or ACL) or meniscus tears, can lead to acute knee pain. Sports-related injuries, falls, or accidents often contribute to these issues.
- Overuse and Strain: Engaging in repetitive activities or putting excessive strain on the knees, especially without proper rest or conditioning, can lead to overuse injuries and chronic pain.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, small sacs that cushion the outside of the knee joint, can cause localized pain and swelling. This condition is known as bursitis.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder, rheumatoid arthritis can affect the joints, including the knees, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Risk Factors for Knee Pain:
Several factors may increase the likelihood of experiencing knee pain:
- Age: Aging is a natural contributor to wear and tear on the joints, making older individuals more prone to conditions like osteoarthritis.
- Weight: Excess body weight places additional stress on the knees, increasing the risk of developing conditions such as osteoarthritis.
- Activity Level: Engaging in high-impact sports or activities without proper conditioning and technique can lead to injuries and chronic knee pain.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to conditions like arthritis, increasing their susceptibility to knee pain.
Managing Knee Pain:
- Rest and Ice: For acute injuries or flare-ups, resting the affected knee and applying ice can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
- Physical Therapy: A tailored exercise program designed by a physical therapist can strengthen the muscles around the knee, improving stability and reducing pain.
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can provide temporary relief. In some cases, prescription medications may be recommended.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on the knees and alleviate symptoms of knee pain.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections may be recommended for managing inflammation and providing relief.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
Persistent or severe knee pain, especially if accompanied by swelling, redness, or difficulty bearing weight, warrants prompt medical attention. A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough evaluation, order imaging studies if necessary, and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Conclusion
Knee pain is a prevalent issue that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and effective management strategies is crucial for individuals seeking relief from this common ailment. By adopting a holistic approach that includes lifestyle modifications, targeted exercises, and, when necessary, medical intervention, individuals can take proactive steps toward maintaining optimal knee health and overall well-being.