Unraveling the Mystery of Shoulder Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Solutions.
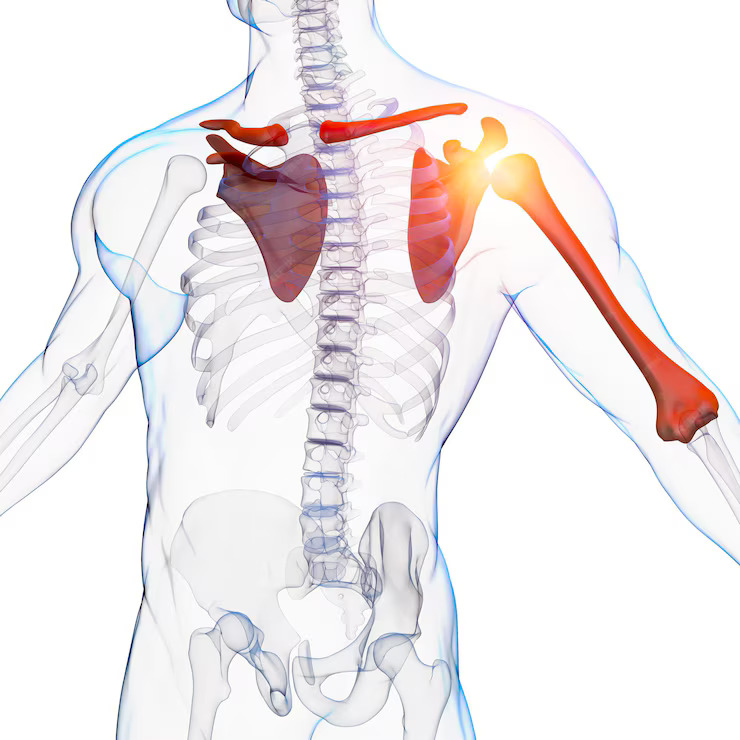
Shoulder pain is a common complaint that can significantly impact daily activities and diminish the overall quality of life. The shoulder is a complex joint, and pain can arise from various causes, ranging from overuse and muscle strain to more serious underlying conditions. Understanding the factors contributing to shoulder pain is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Common Causes of Shoulder Pain
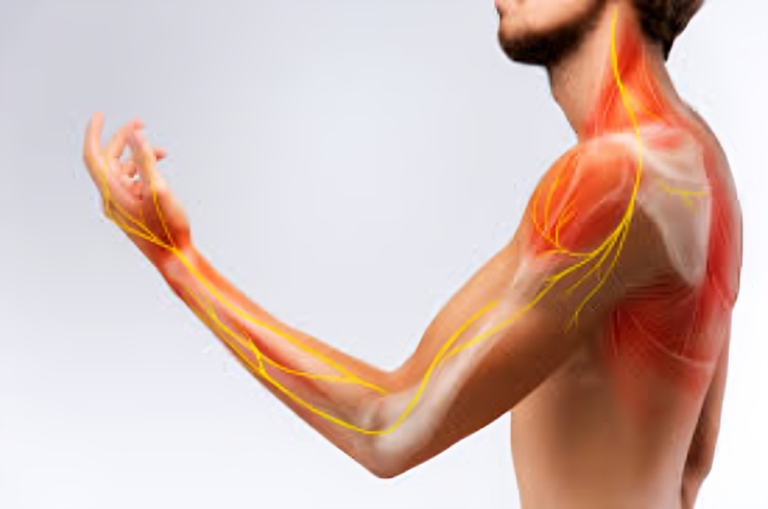
- Rotator Cuff Injuries:
- The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. Injuries, such as tears or strains, can result in pain, weakness, and limited range of motion.
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis):
- Characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint, frozen shoulder often develops gradually and can be linked to inflammation and the thickening of the joint capsule.
- Tendonitis:
- Inflammation of the tendons surrounding the shoulder, known as tendonitis, can occur due to repetitive overhead movements or strain, causing pain and discomfort.
- Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the shoulder joint, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility.
- Bursitis:
- Inflammation of the bursa sac, which cushions the shoulder joint, can cause pain, especially during movement.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Shoulder pain can manifest as a dull ache, sharp pain, or discomfort during specific movements. Diagnosing the cause involves a thorough examination, often including imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans. It’s crucial to provide detailed information about the onset, duration, and nature of the pain for an accurate diagnosis.
Management and Treatment
- Rest and Ice:
- Resting the shoulder and applying ice can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, especially in the case of acute injuries.
- Physical Therapy:
- Targeted exercises and physical therapy can improve shoulder strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Therapists may also employ techniques to address underlying issues.
- Medication:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provide relief from pain and inflammation.
- In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended for more severe symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Avoiding activities that exacerbate pain and adopting ergonomic practices can prevent further strain on the shoulder.
- Surgical Interventions:
- In cases of severe injuries, tears, or conditions that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical options, including arthroscopy or shoulder replacement, may be considered.
Prevention and Self-Care
- Proper warm-up before engaging in physical activities can help prevent muscle strain and injuries.
- Maintaining good posture and avoiding prolonged periods of immobility can contribute to overall shoulder health.
- Regular shoulder exercises that focus on strength and flexibility can reduce the risk of developing pain and discomfort.
Conclusion
Shoulder pain is a common and multifaceted issue that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management. Seeking timely medical attention, incorporating preventive measures, and following a tailored treatment plan can often lead to significant improvement in shoulder pain and enhance overall shoulder joint health.