Understanding Nerve Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options.
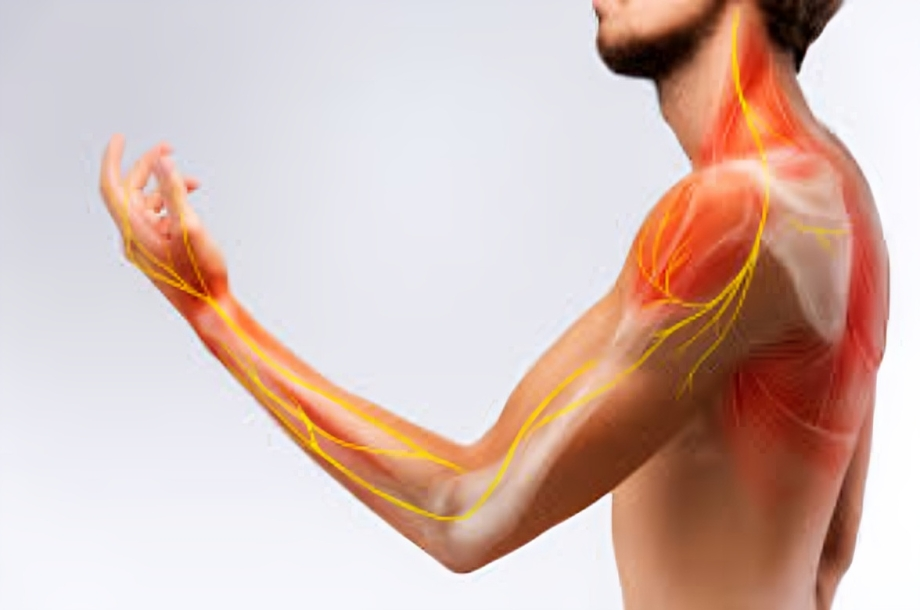
Nerve pain, also known as neuropathic pain, is a complex and often debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Unlike typical pain resulting from physical injuries or inflammation, nerve pain originates from abnormalities or damage in the nervous system. This article aims to shed light on the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options for nerve pain.
To Know More About it Please Click Here
Causes of Nerve Pain
- Peripheral Neuropathy: One of the most common causes of nerve pain is peripheral neuropathy, a condition characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves. Diabetes, infections, certain medications, and traumatic injuries are common contributors to peripheral neuropathy.
- Traumatic Injuries: Nerve pain can also result from injuries such as falls, car accidents, or sports-related incidents. Trauma can damage nerves directly or cause inflammation, leading to persistent pain.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis can trigger the immune system to attack the nerves, causing inflammation and nerve pain.
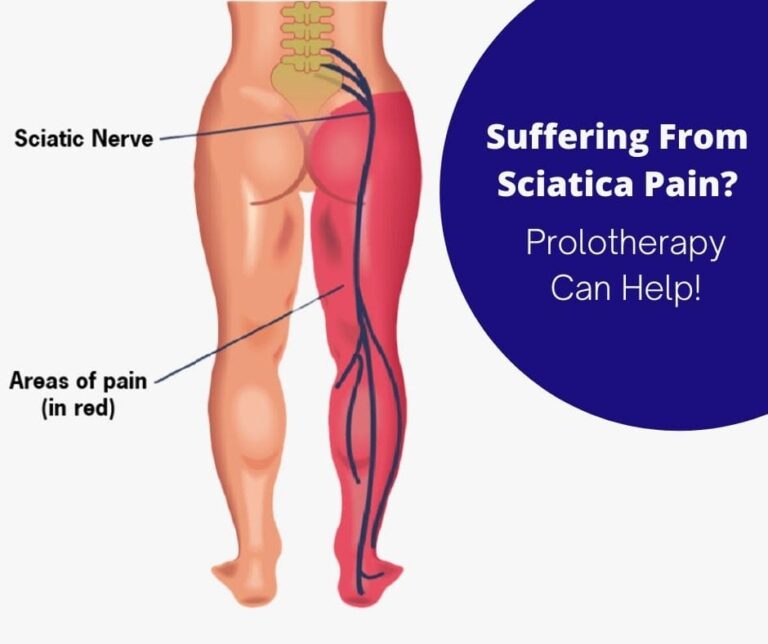
- Herniated Discs: In cases of herniated discs or spinal stenosis, the nerves in the spine may become compressed, resulting in pain that radiates along the affected nerve pathways.
Symptoms of Nerve Pain
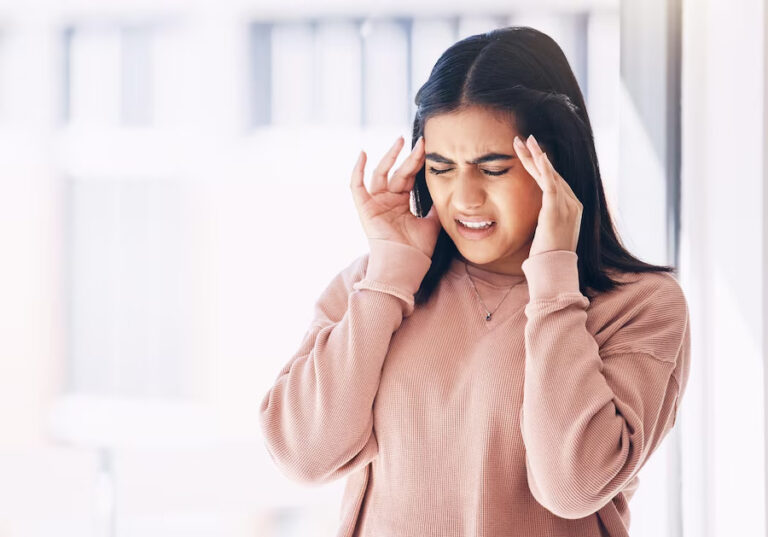
- Burning or Tingling Sensations: Nerve pain often manifests as a burning or tingling sensation, which can be constant or intermittent.
- Sharp or Shooting Pain: Individuals experiencing nerve pain may describe it as sharp, stabbing, or shooting, often radiating along specific nerve pathways.
- Numbness or Weakness: Nerve damage can lead to numbness or weakness in the affected area, impacting motor functions.
- Increased Sensitivity: Some individuals with nerve pain may experience heightened sensitivity to touch or temperature changes.
Treatment Options for Nerve Pain
- Medications:
- Anticonvulsants and Antidepressants: These medications are commonly prescribed to alleviate nerve pain by stabilizing electrical signals in the nerves and modulating neurotransmitters.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications, such as opioids, may be used for short-term relief. However, long-term use carries risks of dependence and side effects.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help manage nerve pain by improving muscle strength, flexibility, and overall mobility. Therapists may also employ techniques like nerve gliding exercises.
- Topical Treatments: Creams, patches, or gels containing medications like lidocaine or capsaicin can be applied to the affected area to provide localized relief.
- Nerve Blocks and Injections: In some cases, healthcare professionals may administer nerve blocks or injections of corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Surgical Interventions: Severe cases of nerve pain, especially those caused by compressed nerves or structural issues, may require surgical interventions such as decompression surgery or nerve repair.
To Know More About it Please Click Here
Conclusion
Nerve pain is a challenging condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring various treatment options are crucial steps in managing and mitigating the effects of nerve pain. It is important for individuals experiencing persistent or severe nerve pain to seek professional medical advice to determine the most appropriate course of action for their specific situation.