Shoulder Pain In Athletes: Sports Injuries And Performance Rehabilitation
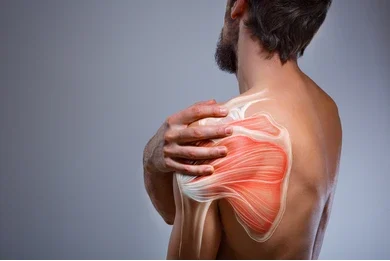
Shoulder pain is a common complaint among athletes participating in various sports, ranging from overhead throwing activities like baseball and softball to contact sports like football and rugby. Injuries to the shoulder can significantly impact an athlete’s performance and quality of life, requiring prompt diagnosis and appropriate rehabilitation to return to play safely. In this article, we explore the unique challenges of shoulder pain in athletes, focusing on sports injuries, rehabilitation strategies, and performance optimization.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Understanding Shoulder Injuries in Athletes
Athletes are particularly susceptible to shoulder injuries due to the repetitive stress, high-impact collisions, and overhead motions associated with sports activities. Common shoulder injuries in athletes include:
Rotator Cuff Tears: Overuse or trauma can cause tears in the muscles and tendons of the rotator cuff, leading to pain, weakness, and limited range of motion.
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: Athletes engaged in repetitive overhead movements may develop shoulder impingement, where the rotator cuff tendons become pinched between the bones of the shoulder, causing pain and inflammation.
Labral Tears: The labrum is a ring of cartilage that lines the socket of the shoulder joint. Labral tears can occur due to acute trauma or repetitive stress, resulting in shoulder instability and pain, particularly in overhead athletes like baseball pitchers.
Shoulder Dislocation/Subluxation: Athletes participating in contact sports or activities with sudden changes in direction may experience shoulder dislocations or subluxations, where the shoulder joint partially or completely comes out of its socket.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Diagnosing shoulder injuries in athletes requires a comprehensive evaluation, including a thorough medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound. Specialized tests like the Neer and Hawkins-Kennedy tests may be performed to assess for impingement or rotator cuff pathology. Additionally, dynamic assessments of shoulder function during sport-specific movements can help identify biomechanical issues contributing to injury.
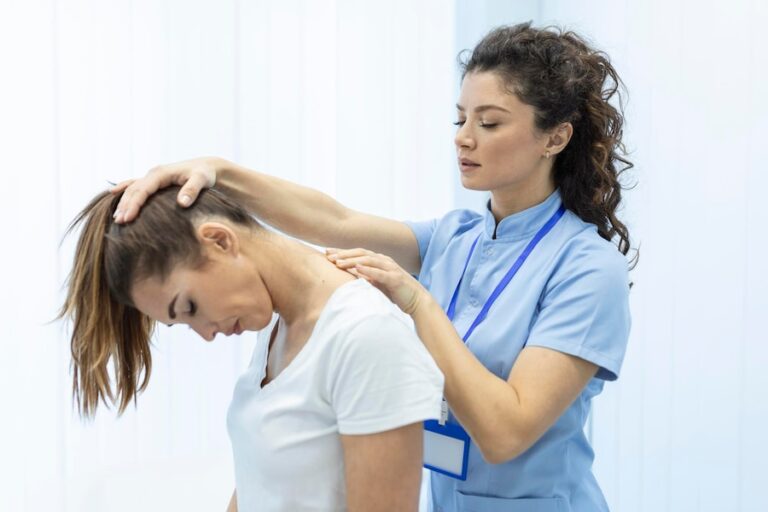
Rehabilitation Strategies for Athletes
Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the management of shoulder injuries in athletes, focusing on pain relief, restoring range of motion, strengthening the shoulder musculature, and improving functional performance. Rehabilitation protocols are tailored to the athlete’s specific injury, sports demands, and stage of recovery but may include:
Pain Management: Modalities such as ice, heat, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation may be used to alleviate pain and inflammation in the acute phase of injury.
Range of Motion Exercises: Gentle stretching and range of motion exercises help maintain flexibility and prevent stiffness in the shoulder joint.
Strength Training: Progressive resistance exercises targeting the rotator cuff, deltoid, and scapular stabilizers help restore muscle strength and endurance.
Functional Training: Sport-specific exercises and drills are incorporated to improve neuromuscular control, proprioception, and dynamic stability of the shoulder.
Biomechanical Analysis: Video analysis of sports-specific movements allows therapists to identify faulty mechanics and implement corrective strategies to reduce the risk of re-injury.
Return to Play Protocol
Returning to sports after a shoulder injury requires a gradual and systematic approach to ensure the athlete’s safety and long-term success. A return-to-play protocol may include progressive strengthening, sport-specific drills, and simulated gameplay under the supervision of a sports medicine professional. Athletes should demonstrate pain-free range of motion, adequate strength and stability, and functional readiness before being cleared for full participation.
Performance Optimization
Beyond injury rehabilitation, athletes can benefit from performance optimization strategies to enhance shoulder health and prevent future injuries. These may include:
Proper Warm-up and Cool-down: Dynamic warm-up exercises and stretching routines help prepare the shoulder muscles for activity and reduce the risk of injury.
Technique Modification: Coaches and trainers can provide instruction on proper body mechanics and techniques to minimize stress on the shoulder joint during sports activities.
Strength and Conditioning: A comprehensive strength and conditioning program focusing on shoulder stability, mobility, and power can improve athletic performance and reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
Cross-training: Incorporating cross-training activities such as swimming, yoga, or Pilates can help maintain overall fitness and balance muscle development, reducing the risk of repetitive stress injuries.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion
Shoulder pain is a common and debilitating problem for athletes, affecting performance and participation in sports activities. By understanding the unique challenges of shoulder injuries in athletes and implementing evidence-based rehabilitation strategies, athletes can achieve optimal recovery and return to play safely. With proper diagnosis, rehabilitation, and performance optimization, athletes can overcome shoulder injuries and continue to pursue their athletic goals with confidence and resilience. Through collaboration between athletes, coaches, trainers, and sports medicine professionals, we can promote shoulder health and injury prevention in the athletic community, ensuring long-term success and longevity in sports participation.