Nerve Pain in Multiple Sclerosis: Understanding the Impact
Nerve pain, also known as neuropathic pain, can manifest in various forms and intensities, often associated with specific medical conditions. Unlike other types of pain, nerve pain originates from dysfunction or damage to the nervous system itself, rather than from external injuries or inflammation. Understanding nerve pain within the context of specific conditions is crucial for effective diagnosis, treatment, and management. In this article, we delve into some common conditions associated with nerve pain, exploring their causes, symptoms, and potential treatment approaches.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that occurs in individuals with diabetes. High levels of blood sugar over time can damage the nerves throughout the body, leading to symptoms such as tingling, numbness, burning sensations, and sharp pains, typically starting in the feet and hands and gradually spreading upwards. Controlling blood sugar levels through medication, lifestyle changes, and maintaining a healthy diet is crucial in managing diabetic neuropathy. Additionally, medications targeting nerve pain, such as certain antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and topical treatments, may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage to the peripheral nerves, which transmit signals between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body. This condition can result from various causes, including diabetes, infections, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications. Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy may include weakness, numbness, tingling, and sharp, shooting pains, often in the hands and feet. Treatment approaches may involve addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms with medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
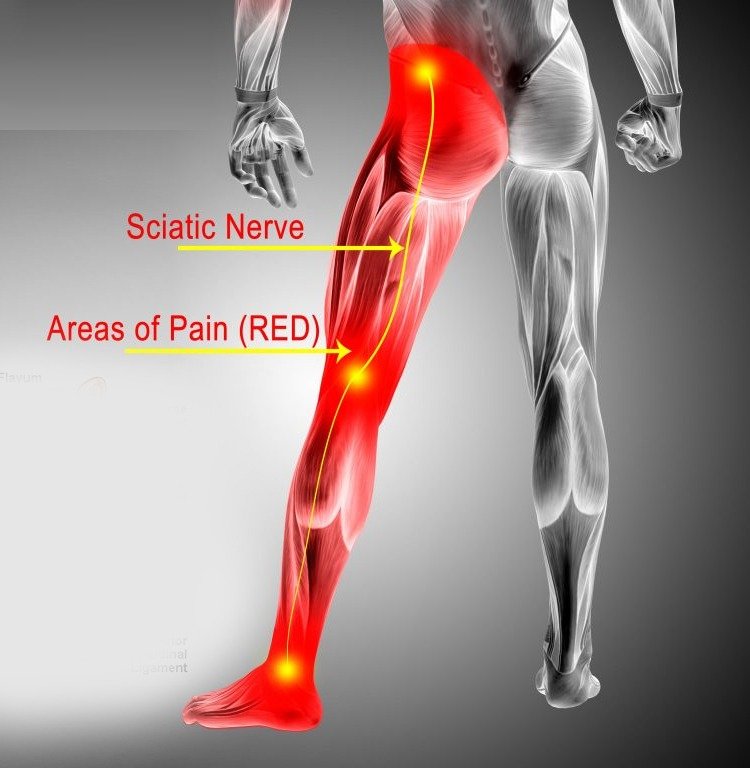
Sciatica
Sciatica is a specific type of nerve pain that originates from compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down through the buttocks and legs. Common causes of sciatica include herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or muscle spasms in the lower back. Symptoms typically include sharp, shooting pain that radiates from the lower back down one leg, along with numbness, tingling, and weakness. Treatment for sciatica often involves a combination of pain medications, physical therapy, stretching exercises, and in some cases, epidural steroid injections or surgery to relieve pressure on the affected nerve.
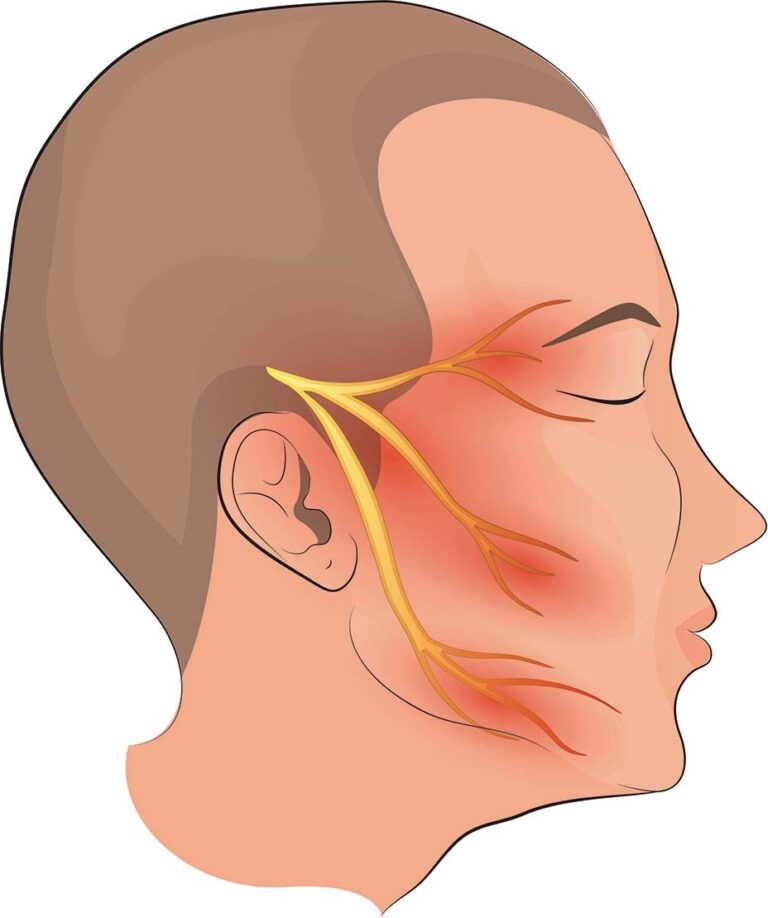
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition affecting the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for sensations in the face. This condition is characterized by sudden, severe facial pain described as stabbing or electric shock-like sensations, typically triggered by mundane activities such as eating, talking, or touching the face. Trigeminal neuralgia can be debilitating and significantly impact the quality of life. Treatment options may include medications such as anticonvulsants or muscle relaxants, nerve blocks, and in severe cases, surgery to alleviate pressure on the trigeminal nerve.
Postherpetic Neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia is a complication of shingles, a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which also causes chickenpox. After recovering from shingles, some individuals may experience persistent nerve pain in the affected area, known as postherpetic neuralgia. This condition is characterized by burning, stabbing, or throbbing pain, often accompanied by sensitivity to touch. Treatment may involve antiviral medications, pain relievers, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, topical treatments, and nerve blocks to manage symptoms.
Conclusion
Nerve pain associated with specific medical conditions can be challenging to manage, often requiring a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals from various specialties. Proper diagnosis, understanding the underlying cause, and tailoring treatment strategies to individual needs are essential in effectively managing nerve pain. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep, can play a crucial role in minimizing symptoms and improving overall well-being for individuals living with nerve pain. If you experience persistent or severe nerve pain, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.
Also, Follow us on Instagram